FOOD SAFETY AND QUALITY
Natural Antimicrobials: Bacteriocin Applications in Foods


Commercial bacteriocins, bioactive powders, and bacteriocin-producing cultures are being used in fermented meats and dairy products. © Lauri Patterson/ E+/Getty Images
Since their discovery almost a century ago, bacteriocins have been recognized as promising antimicrobial agents with possible food, clinical, and veterinary applications.
Bacteriocins are toxic proteins produced by a given strain of bacteria that are active against closely related species but not on the producer organism (Perez et al. 2014). As natural antimicrobials, bacteriocins are an appealing alternative to chemical antimicrobials in the wake of continuing consumer demand for ready-to-eat, convenient, and more “natural” foods that use fewer chemical antimicrobials to control microbial growth (Verma et al. 2014).
In addition, several bacteriocins are potential alternatives to conventional antibiotics used to treat human infections, especially antibiotic-resistant infections (Ng et al. 2020, Shin et al. 2016). Some other bacteriocins have documented anticancer (Zimina et al. 2020, Yang et al. 2014) or antiviral activities (Soltani et al. 2021), and select bacteriocins promote animal growth and/or control bacterial infections in cattle, swine, and poultry production (Hernández-González et al. 2021, Ng et al. 2020).
Biologically Based Preservation
Biologically based preservation—biopreservation—methods that do not ferment foods are among the newest methods of food preservation. Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and their metabolites are used in biopreservation because LAB have biopreservation capabilities that other foodborne bacteria lack, in addition to generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. While biopreservation largely focuses on foods that are not fermented, LAB bacteriocins can also enhance fermented food quality by preventing undesirable bacteria growth and stimulating growth of the starter cultures used in fermentation.
The use of bacteriocins as biopreservatives has several reported benefits (Gálvez et al. 2007):
- Longer shelf life for foods
- Additional safety during potential temperature abuse
- Reduced risk of contamination by foodborne pathogens during food processing and/or storage
- Reduced economic losses from food spoilage, voluntary and mandatory food product recalls, and foodborne illness outbreaks
- Use of minimal processing without compromising microbial food safety, allowing better retention of macro- and micronutrients and enabling preservation of desirable organoleptic properties of foods
Because bacteriocins are colorless, odorless, and flavorless molecules, they do not change sensory, chemical, or physical properties of foods.
Bacteriocin Food Applications
Because bacteriocins are colorless, odorless, and flavorless molecules, they do not change sensory, chemical, or physical properties of foods. Several bacteriocins are functional at low pH values, a broad range of salt concentrations, and high temperatures, so they can be used in applications in a wide variety of food products (Perez et al. 2014).
Bacteriocins can be applied to foods in various forms (Figure 1): 1) partially purified bacteriocins; 2) fermented products (fermentates) containing bacteriocins; 3) bacteriocin-producing (bacteriocinogenic) cultures, such as BioSafe; and 4) bacteriocins incorporated into coatings and packaging films (da Costa et al. 2019). The application of partially purified bacteriocins and fermentates has been more common due to their efficacy (Silva et al. 2018).
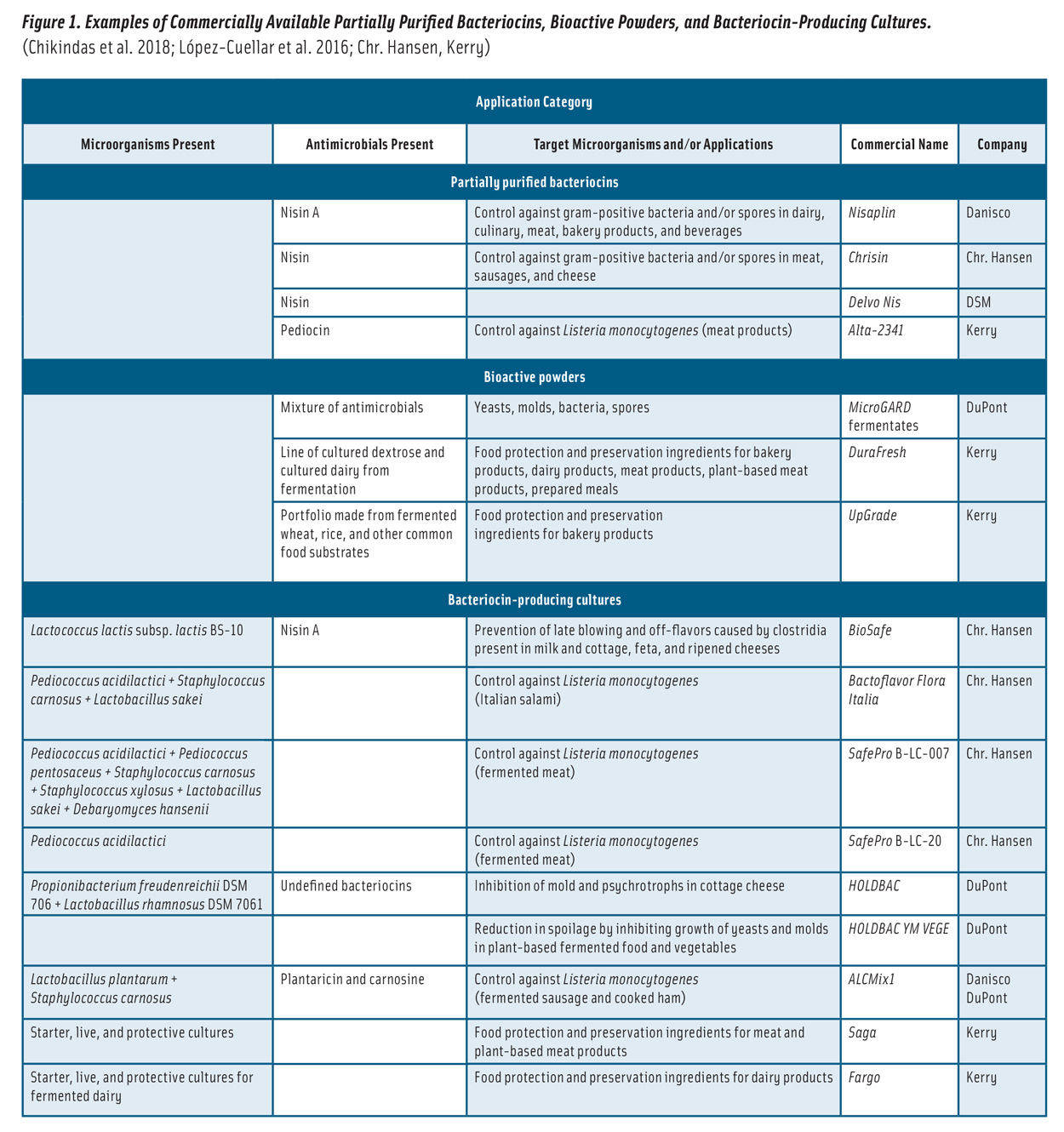
Figure 1. Examples of Commercially Available Partially Purified Bacteriocins, Bioactive Powders, and Bacteriocin-Producing Cultures. (Chikindas et al. 2018; López-Cuellar et al. 2016; Chr. Hansen, Kerry)
LAB Bacteriocins
Nisin, produced in several natural variants by Lactococcus and Streptococcus species, is the first and best characterized bacteriocin from LAB. It is the only bacteriocin licensed in more than 50 countries as a biopreservative (Shin et al. 2016, Verma et al. 2014) and is sold as a partially purified product of dairy or nondairy fermentations, marketed under names such as Nisaplin, Chrisin, and Delvo Nis (Figure 1).
Many factors affect the activity of nisin against bacterial spores, including temperature and pH, and nisin is a more effective antimicrobial at lower temperatures and under acidic conditions. In addition, nisin is often used in combination with other technologies such as thermal processing, modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), high pressure processing, pulsed electric fields, and other antimicrobials (Silva et al. 2018). For example, the refrigerated shelf life of liquid whole eggs extends from 6–11 days to 17–20 days when nisin is added, at a concentration of 5 mg/ml, before pasteurization. In fresh fish packaged in an atmosphere of CO2, nisin extends the shelf life and, more importantly, delays botulinum toxin production by Clostridium botulinum type E strains. The combination of nisin and MAP is more effective in preventing growth by Listeria monocytogenes on raw pork compared with nisin or MAP use on its own (Montvile and Chikindas 2013).
Nisin is widely used to control C. botulinum spores as well as L. monocytogenes cells, although L. monocytogenes cells are much more sensitive to nisin than C. botulinum spores are. While 200 IU/ml nisin is sufficient to reduce L. monocytogenes cells by 6 logs, 10,000 IU/ml nisin is required to reduce C. botulinum spores at a similar level (Montville and Chikindas 2013). Nisin prevents biofilm formation by L. monocytogenes. It also sensitizes C. botulinum spores to heat, resulting in potentially reduced thermal treatments of foods—an application approved in some countries but not in the United States (Matthews et al. 2017).
L. monocytogenes can also be inhibited by pediocins and pediocin-like bacteriocins, which are small heat-stable proteins produced by LAB. Pediocin PA-1, pediocin AcH, sakacins (A and P), leucocins A, bavaricin MN, and curvacin A are well-studied bacteriocins in this group. As covered by European patents, pediocin PA-1 can be used to extend shelf life of salads and salad dressings and to ensure safety of cream cheese, cottage cheese, meats, and salads against growth by L. monocytogenes (Montville and Chikindas 2013).
Bioactive Powders
Bacteriocins can be incorporated into food products as bioactive powders, especially when a concentrated form of natural antimicrobial is needed. These bioactive powders often contain a mixture of antimicrobial compounds (bacteriocins, organic acids, etc.). Powders are usually derived from cultivating the producer strain in an appropriate microbiological growth medium, followed by heat inactivation of the bacterial cells and then drying the medium (Soltani et al. 2021).
Commercial bioactive powders, such as MicroGARD, are effective against an array of yeasts, molds, and bacteria (Figure 1).
What’s Ahead
Successfully adding specific bacteriocins to foods may be limited because of a narrow spectrum of antimicrobial activity as well as poor solubility, slow diffusion, uneven distribution, and partitioning in the food matrix. Using encapsulation technologies, as well as incorporating bacteriocins into coatings and packaging films and applying bacteriocins on food surfaces, has been successful in overcoming such limitations (da Costa et al. 2019, Ünlü et al. 2015).
Since nisin received GRAS status from FDA in 1988 (FDA 2021), numerous bacteriocins with unique structures and diverse modes of antimicrobial activity have been discovered and reported. Further research is necessary on the safety, production, and prospective applications of these bacteriocins. Extensive research on bacteriocin immunogenicity and toxicity, for example, is essential to confirm bacteriocin safety, and clinical studies are needed for approval of bacteriocins by the World Health Organization and regulatory agencies such as FDA. This is an exciting time for basic and applied bacteriocin research and development that will lead to future applications in food biopreservation as well as clinical and veterinary applications of bacteriocins.
Learning Objectives
- Biologically based preservation (biopreservation) methods that do not ferment foods are among the newest methods of food preservation.
- Bacteriocins can be applied to foods in various forms: 1) partially purified bacteriocins; 2) fermented products (fermentates) containing bacteriocins; 3) bacteriocin-producing (bacteriocinogenic) cultures; and 4) bacteriocins incorporated into coatings and packaging films.
- The first and best-characterized bacteriocin from lactic acid bacteria is nisin.
Glossary
Biopreservation: A modern food preservation method that deals with application of lactic acid bacteria and their metabolites—bacteriocins in particular—in nonfermented foods.
Bacteriocin: Ribosomally synthesized antimicrobial proteins produced by bacteria that are active against closely related bacteria but not on the producer organism.
Nisin: A bacteriocin with GRAS (generally recognized as safe) designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, widely used to control Clostridium botulinum spores as well as Listeria monocytogenes cells.
Pediocin: A bacteriocin that is effective against L. monocytogenes cells.
REFERENCES
Chikindas, M. L., R. Weeks, D. Drider, et al. 2018. “Functions and Emerging Applications of Bacteriocins.” Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 49: 23–28. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2017.07.011.
da Costa, R. J., F. L. S. Voloski, R. G. Mondadori, et al. 2019. “Preservation of Meat Products with Bacteriocins Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Meat.” J. Food Qual.: 4726510. doi: 10.1155/2019/4726510.
FDA. 2021. “Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS).” https://www.fda.gov/food/food-ingredients-packaging/generally-recognized-safe-gras.
Gálvez A., H. Abriouel, R. L. López, et al. 2007. “Bacteriocin-Based Strategies for Food Biopreservation.” Int. J. Food Microbiol. 120 (1–2): 51–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2007.06.001.
Hernández-González, J. C., A. Martínez-Tapia, G. Lazcano-Hernández, et al. 2021. “Bacteriocins from Lactic Acid Bacteria. A Powerful Alternative as Antimicrobials, Probiotics, and Immunomodulators in Veterinary Medicine.” Animals 11(4): 979. doi: 10.3390/ani11040979.
López-Cuellar, M. R., A.-I. Rodríguez-Hernández, and N. Chavarría-Hernández. 2016. “LAB Bacteriocin Applications in the Last Decade.” Biotechnol. Biotechnologic. Equip. 30(6): 1039–1050. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2016.1232605.
Matthews, K. R., K. E. Kniel, and T. J. Montville. 2017. “Biologically Based Preservation and Probiotic Bacteria.” Chpt. 26 in Food Microbiology: An Introduction, edited by K. R. Matthews, K. E. Kniel, and T. J. Montville. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press.
Montville, T. J. and M. L. Chikindas. 2013. “Biological Control of Foodborne Bacteria.” Chpt. 31 in Food Microbiology: Fundamentals and Frontiers, edited by M. P. Doyle and R. L. Buchanan. Washington, D.C.: ASM Press.
Ng, Z. J., M. A. Zarin, C. K. Lee, et al. 2020. “Application of Bacteriocins in Food Preservation and Infectious Disease Treatment for Humans and Livestock: a Review.” RSC Adv. 10: 38937–38964. doi: 10.1039/D0RA06161A.
Perez, R. H., T. Zendo, and K. Sonomoto. 2014. “Novel Bacteriocins from Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB): Various Structures and Applications.” Microb. Cell Fact. 13: S3. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-13-S1-S3.
Shin, J. M., J. W. Gwak, P. Kamarajan, et al. 2016. “Biomedical Applications of Nisin.” J. App. Microbiol. 120(6): 1449–1465. doi: 10.1111/jam.13033.
Silva, C. C. G., S. P. M. Silva, and S. C. Ribeiro. 2018. “Application of Bacteriocins and Protective Cultures in Dairy Food Preservation.” Front. Microbiol. 9: 594. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00594.
Soltani, S., R. Hammami, P. D. Cotter, et al. 2021. “Bacteriocins as a New Generation of Antimicrobials: Toxicity Aspects and Regulations.” FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 45(1): fuaa039. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa039.
Ünlü, G., B. Nielsen, and C. Ionita. 2016. “Inhibition of Listeria monocytogenes in Hot Dogs by Surface Application of Freeze-Dried Bacteriocin-Containing Powders From Lactic Acid Bacteria.” Prob. Antimic. Prot. 8(2): 102–110. doi: 10.1007/s12602-016-9213-2.
Verma, A. K., R. Banerjee, H. P. Dwivedi, et al. 2014. “Bacteriocins: Potential in Food Preservation.” Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, edited by C. A. Batt and M. L. Tortorello. Cambridge, Mass.: Academic Press.
Yang, S. C., C.-H. Lin, C. T. Sung, et al. 2014. “Antibacterial Activities of Bacteriocins: Application in Foods and Pharmaceuticals.” Fron. Microbiol. 5: 241. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00241.
Zimina, M., O. Babich, A. Prosekov, et al. 2020. “Overview of Global Trends in Classification, Methods of Preparation and Application of Bacteriocins.” Antibiotics 9(9): 553. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9090553.
Authors
-
Gülhan Ünlü
Categories
-
Food Safety and Defense
-
Food Ingredients and Additives
-
Pathogens
-
Shelf Life
-
Food Quality
-
Spoilage Microorganisms
-
Food Technology Magazine



