Outlook 2025: Technology Trends

Technology—“the great growling engine of change” as American futurist Alvin Toffler aptly described it—continues to trend strongly toward digitization across manufacturing sectors, especially in the consumer packaged goods category. In the food and beverage industry, the outlook for advanced technology applications might be described, à la Toffler, as a loud and rumbling growl. Tech innovation is steadily chugging along as digital solutions improve productivity gains in all areas of global food systems and businesses, including product development.
In addition to researching and monitoring food and beverage technology trends over the past year, Food Technology surveyed IFT member food, beverage, and ingredient manufacturers, industry consultants, and technology developers to capture trend indicators for 2025. Nearly 200 participants ranked the technologies they think are most promising to transform food production, manufacturing, and distribution to ensure safe, nutritious, and sustainable products for all consumers. This year’s Technology Outlook is informed by survey responses to questions about the technologies companies expect to invest in during 2025, what’s driving those investments, and the benefits they expect to gain.
Digital Transformation Tech
In 2024, the number of digital transformation solutions on the market has mushroomed, giving the food and beverage industry lots of options for improving and even revolutionizing operational productivity and performance. Although still a nascent technology, use cases of artificial intelligence (AI) in the food industry have proliferated in the past year. Notable applications include fueling the development of novel proteins and functional foods aligned with current market demands and dietary preferences and improving manufacturers’ ability to monitor and track food products to ensure the quality and safety of food products in near real-time.
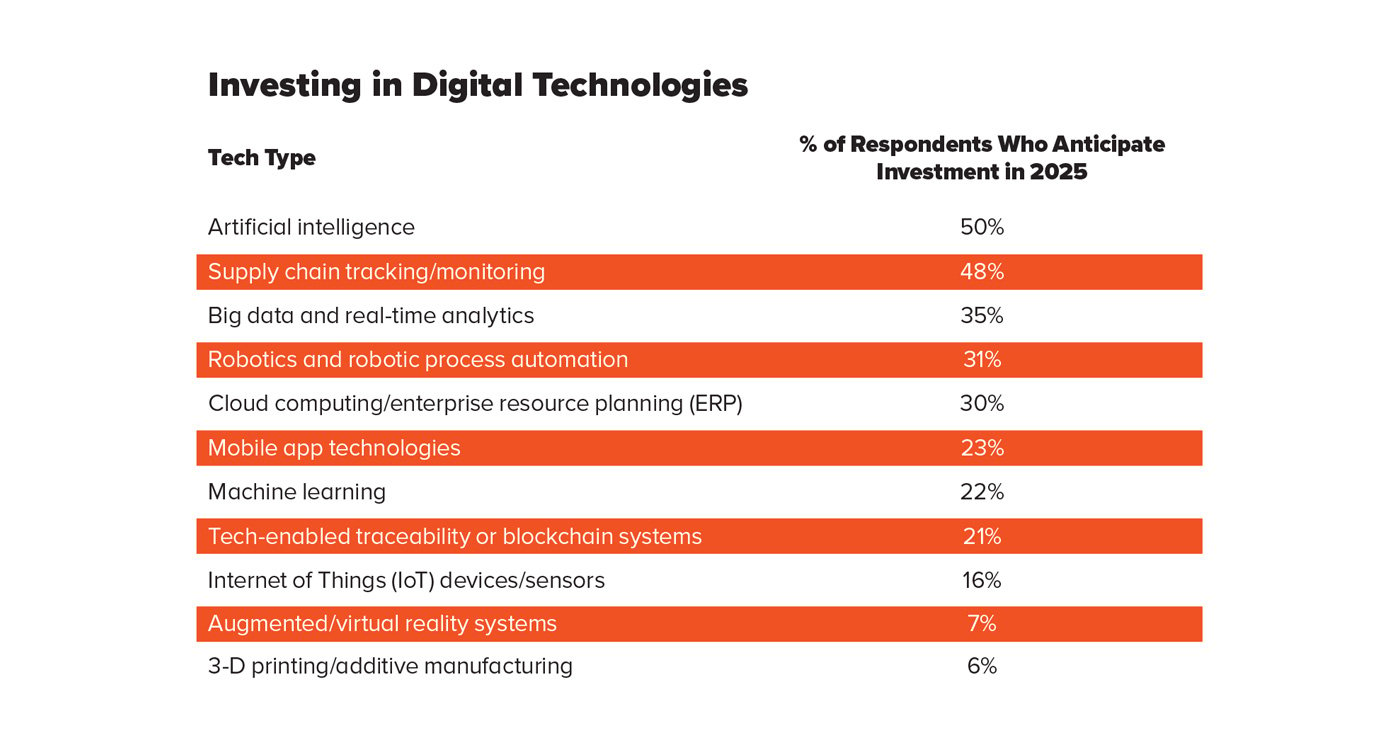
About half of industry professionals who responded to Food Technology’s Technology Trends Survey say their companies plan to invest in AI (50%) and/or supply chain tracking systems (48%) as part of their digital transformation strategies in 2025. The next most popular technologies, targeted for investment by about one-third of respondents, are big data and real-time analytics, robotics and process automation, and cloud computing and enterprise resource planning software and systems. Food, beverage, and ingredient companies also are expected to invest in mobile app technologies (23%), machine learning software (22%), tech-enabled traceability systems (21%), and Internet of Things (IoT) devices (16%).
When asked about which business processes have been most positively impacted by their companies’ adoption of digital transformation technologies, respondents strongly indicate four: manufacturing process/assembly (34%), food safety preventive control (28%), supply chain production control (26%), and inventory/warehouse management (19% and 11%, respectively).
Survey respondent Renee Perry, vice president of corporate social responsibility & environmental, social, governance at sushi ingredient supplier Culimer USA, is not surprised that digital transformation technologies as a whole rank so highly for investment in the coming year. She says that Culimer’s primary technology investment today is in digital technologies, with a focus on tech-enabled traceability systems and devices.
“This shift is driven by the increasing demand for transparency and accountability across the global seafood supply chain,” Perry states. “By adopting advanced traceability platforms, we aim to meet the industry’s evolving standards for sustainability and regulatory compliance for food safety and quality.”
The biggest benefit the company expects to gain from implementing the Global Dialogue on Seafood Traceability through technology powered by GS1 standards is a dramatic improvement in traceability and transparency across its supply chain, she adds. “By ensuring data interoperability, we can seamlessly track seafood products from the first mile—when the product is harvested—all the way to retail, providing a clear and verified account of the product’s journey, [which means] we can share real-time data with partners and regulators globally. The automated data exchange also minimizes manual errors, speeding up processes like audits and customer inquiries, which in turn boosts operational efficiency.”
Approximately half of Technology Trends Survey respondents cite the need to improve production efficiencies (51%), cost efficiencies (45%), and the ability to gather, analyze, and leverage data for data-driven decision-making (47%) as the top three drivers for digital transformation technology investment by their companies or clients in the food, beverage, and ingredient industry. Also driving adoption of Industry 4.0 solutions is the need to reduce labor costs (34%), followed by improving supply chain visibility (17%), agility to respond to trends or changing market conditions (16%), enhancing sustainability goals such as reducing food waste and streamlining upcycling/recycling processes (16%), and increasing transparency across internal operations (16%).
Survey respondent William Melnyczenko, global business development director, digital and expert partners, Mérieux NutriSciences, noted that digital transformation technologies such as AI and software that provide real-time ability to detect microbial load in food commodities and finished products is enabling producers to “shift which suppliers they use, what they allow into their supply chain, and ultimately help them become more efficient and reduce risk.
“We’ve seen significant growth in software designed to automate manual processes like environmental monitoring, supplier management, and audit tracking,” says Melnyczenko. “Companies of all sizes are increasingly looking to standardize and digitize their data, as this helps them manage costs more effectively, gain deeper insights into trends, and focus on their core business rather than data management.”
Biotechnology
The field of food biotechnology, which leverages living organisms or their products to enhance food safety, nutrition, and taste, continues to trend upward as advances in technologies such as fermentation and molecular biology evolve. Among the innovations in this area in the past few years are precision fermentation and enzymatic technology applications, which are creating functional foods that offer additional health benefits beyond basic nutrition, the development of sustainable alternative protein sources such as cultivated meat and plant-based meat substitutes to address food security and environmental concerns, and ways to extend the shelf life of foods without the need for artificial preservatives.
According to Technology Trends Survey respondents, food, beverage, and ingredient companies are most likely to invest in precision fermentation and biochemical technologies in this category in 2025 (22% and 21%, respectively). Among those who forecast their companies will invest in biotechnology applications next year, 17% expect to spend on metabolic, enzymatic, or microbial food and ingredient processing technologies, followed by bioactive compound (14%) and traditional fermentation (13%) technologies.
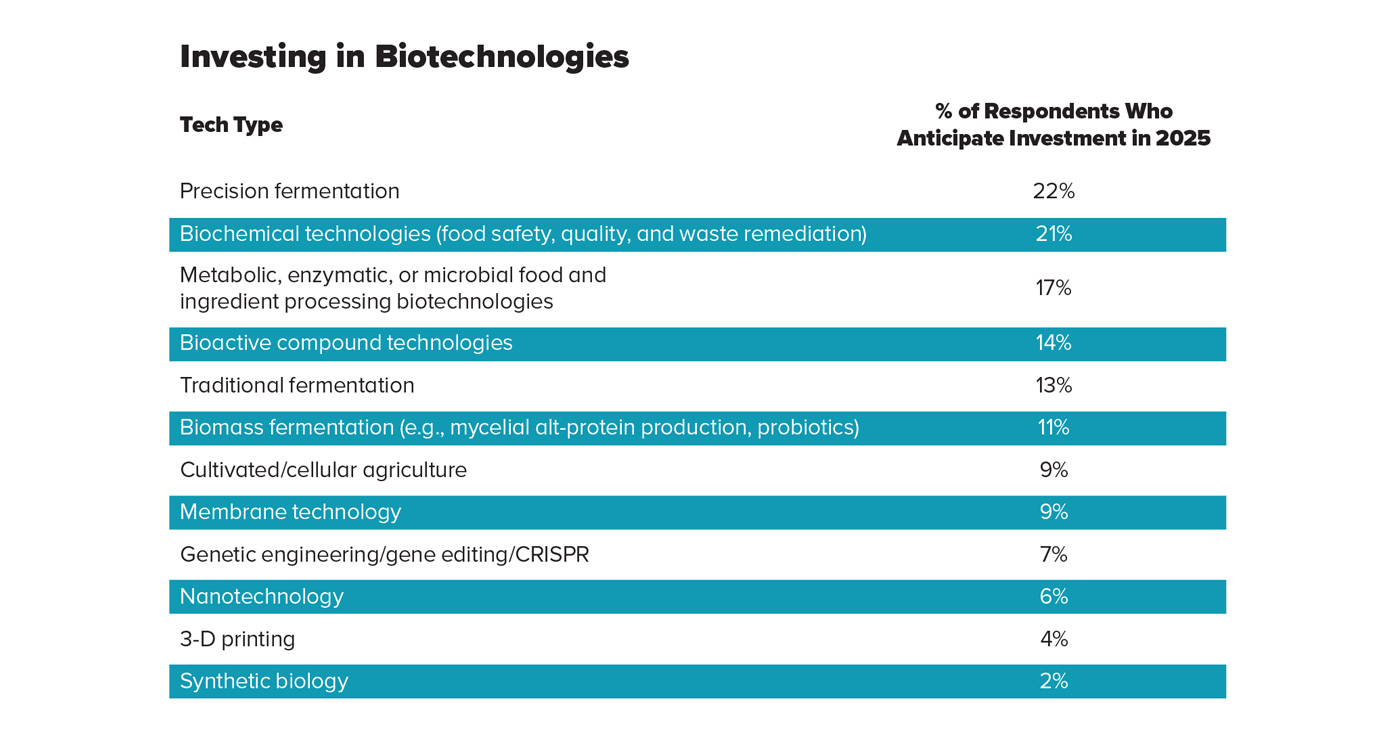
The top three drivers for investment in various biotechnologies indicated in the survey results are achieving new or improved product functionalities such as bioactive compounds for health, longevity, or food security (48%), enhancing flavor, texture, and nutritional value of food products (45%), and gaining process and cost efficiencies (42%). According to the Technology Trends Survey, other reasons that food and ingredient companies are looking to biotechnology solutions include improving extended product shelf life (27%), developing environmental/climate-friendly functionalities such as pest-, drought-, or virus-resistant crops (20%), and fueling business growth or innovation (19%).
Food industry investment in biotechnologies is steadily increasing in tandem with the state of digital transformation systems in food, beverage, and ingredient companies, says Cindy Stewart, food scientist and founder of Innovative Food Science Consulting. “Biotechnology applications, whether it’s fermentation or enzymatic and microbiology methods, have been used for decades in the food industry. But digital technology combined with biotechnology is making methods like precision fermentation, especially in the cultivated meat space, easier and faster to create new products that taste good and are at price parity with products already in the market.”
Sustainable Systems Tech
Sustainability initiatives have played prominent roles in corporations’ core strategies of late as companies look to meet net zero goals by 2030 and respond to mounting government and consumer pressure to reduce energy and water consumption. Add to that the real business benefits of monitoring energy used, carbon emissions, and waste throughout the value chain, and it’s not surprising that technologies that help producers, processors, and distributors achieve production efficiencies while reducing food waste and their impact on the environment are on trend for 2025.
About half of Technology Trends Survey responders say their companies plan to invest in technologies that improve energy and water/wastewater use, conservation, and reduction efficiencies. The next most popular technologies in which respondents expect increased investment in 2025 are carbon emission reduction (36%), upcycling/recycling (30%), and supply chain traceability (27%) technologies.
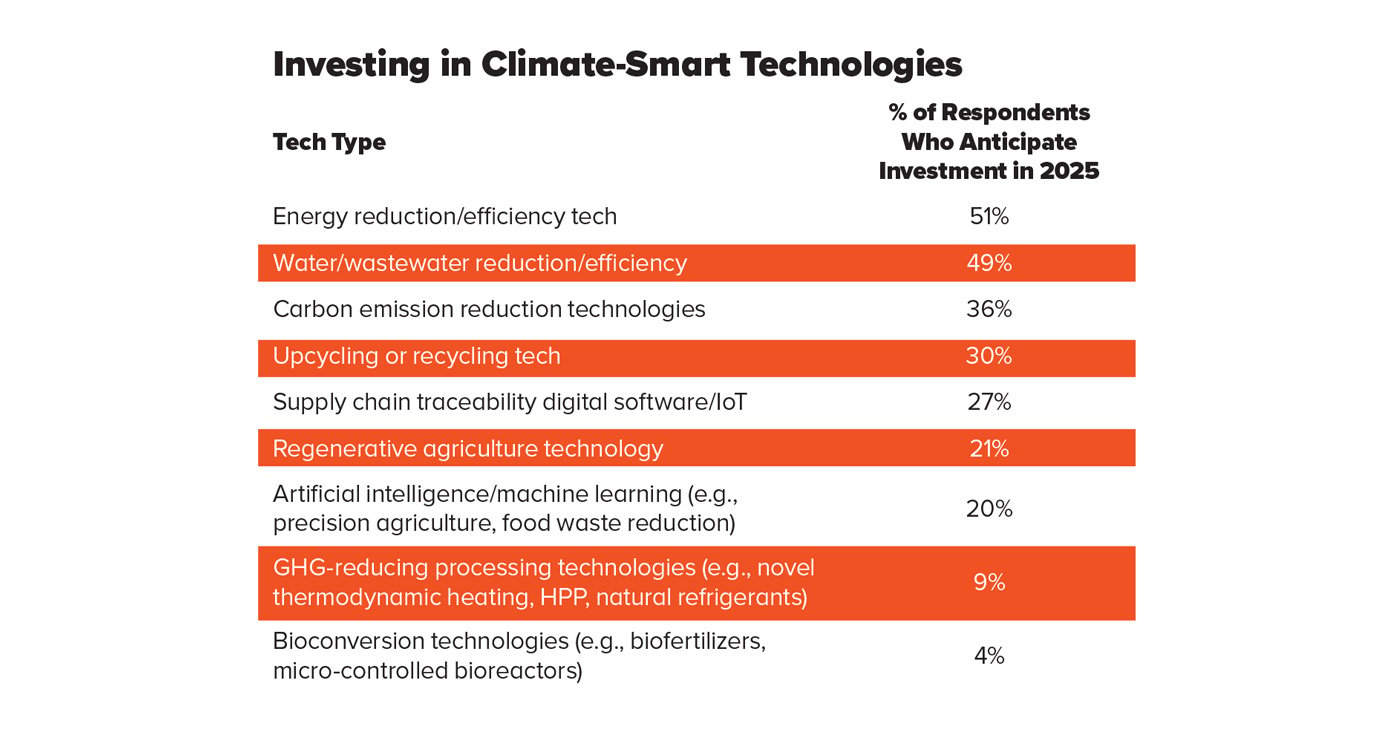
What’s driving this strong interest in sustainable food systems technologies? According to the survey, the top two drivers are meeting consumer demand/preference for sustainable foods (52%) and cost-savings via production efficiencies and maximized throughput (43%). Also driving investments in climate-smart and sustainability technologies are the need to meet internal company sustainability goals (32%), to comply with government regulations (31%), and to contribute to a more sustainable, environmentally friendly future and enhance brand image (32% and 30%, respectively).
Yadu Dar, vice president of business development, Plantible Foods, a startup that makes functional plant-based protein from lemna leaf, says that the company is investing in ways to reinvent agriculture to produce protein-based ingredients to boost functionality and nutrition. “We are doing this by leveraging innovative and sustainable manufacturing practices, harnessing the sun as an energy source, and developing protein isolation techniques that use minimal processing to maintain the integrity and nutritional characteristics of the harvested protein.”
Packaging Tech
Consumers are more focused than ever on product sustainability, and that includes the packaging of the foods they eat. For the foreseeable future, consumer demand and food packaging laws and regulations will continue to drive the adoption of new technologies and materials in this space. For example, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA’s) Food Safety and Modernization Act and consumer demand for transparency and accountability are driving the adoption of intelligent packaging, which includes features like freshness indicators and temperature control. Regulatory bodies are likely to introduce stricter guidelines on the use of plastics and promote the adoption of eco-friendly materials in the coming year. In addition, the advent of packaging extended producer responsibility policies, which hold manufacturers responsible for the management of their products throughout their entire life cycle, including disposal, are beginning to take hold in the United States.
Nearly 30% of Technology Trends Survey industry respondents indicated that they plan to invest in flexible packaging and packaging materials, coatings, and films in 2025. Food, beverage, and ingredient companies surveyed also expect continued near-term investment in bioplastic/biopolymer packaging (23%), aseptic packaging (20%), and modified atmosphere packaging (15%).
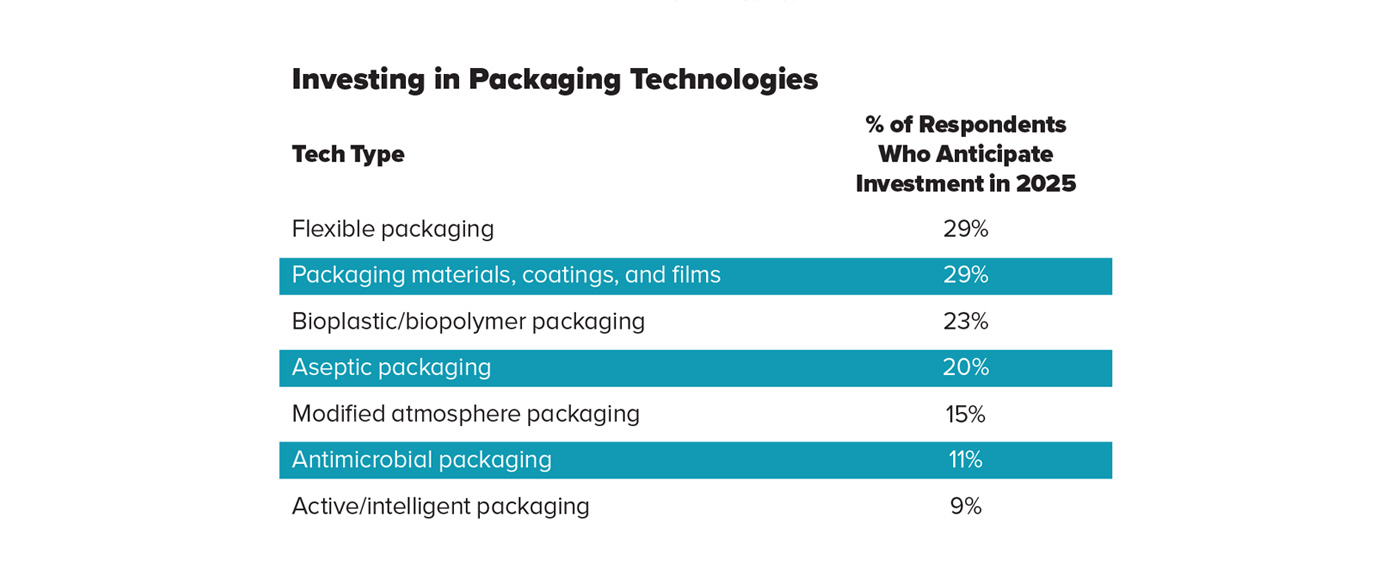
Meeting consumer demand for convenient, minimally packaged food and beverage products (43%) is high on the list of packaging investment drivers for 2025, according to the survey, followed by the need to reduce food packaging in the municipal solid waste stream (29%). About one-quarter of industry respondents noted several other reasons for near-term investment in food packaging by their companies, including to meet internal sustainability goals (25%), extend shelf life/reduce product deterioration time (22%), comply with regulations (22%), improve packaging functionality (22%), and enhance food safety and quality (21%).
“Companies are investing in innovative packaging solutions made from renewable, recyclable, or biodegradable materials to reduce the environmental impact of food packaging,” says survey respondent Rick Falkenberg, founder and chief technical officer of Food Safety & Process Technology Group. “Among the benefits are reduced waste and environmental pollution associated with traditional food packaging, enhanced brand reputation and consumer appeal through eco-friendly packaging, and cost savings from using more affordable and renewable packaging materials.”
Food Safety Tech
With a spate of highly publicized national recalls of foods contaminated with Listeria, Salmonella, and other harmful pathogens in 2023 and 2024, renewed interest in pathogen intervention, control, and other food safety technologies is trending for 2025. Most recently, the Boar’s Head recall of more than 7 million pounds of Listeria-contaminated liverwurst that sickened 57 people and killed 10 in five states was named the largest listeriosis outbreak since the 2011 outbreak linked to cantaloupe. And over the past few years, pathogen-related outbreaks and recalls have affected a broad range of food categories, from ready-to-eat salads, apple juice, and cantaloupe to eggs, cheese, infant formula, and creamer, yogurt, and dough ingredients.
In addition, newer food safety regulations and proposed final rules are driving the trend for many in the food industry, including the January 2026 compliance deadline for the FDA’s Food Traceability Rule, which aims to allow for faster identification and rapid removal of potentially contaminated food from the market, resulting in fewer foodborne illnesses and/or deaths, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Salmonella Framework for Raw Poultry Products proposed rule designed to reduce Salmonella illnesses linked to raw poultry products.
“Although food additives and chemicals as food safety concerns have been in the news of late, most potentially deadly foodborne illnesses are associated with microbiological or pathogenic food contamination,” notes Tracy Fink, IFT director of scientific programs and science & policy initiatives. “Food companies are definitely looking at how they can more efficiently use pathogen intervention and control technologies like high pressure processing and ultraviolet light for food and food-contact surface sanitation and microbial reduction and utilizing next-generation pathogen identification and detection methods to ensure their food safety measures are effective.”

Coupling food safety systems with digital technologies like AI and machine learning has already been shown to improve food safety in predictive maintenance of equipment for sanitation, like finding microbial harborage points based on real-time and historical data points and predictive modeling, Fink adds. These digital technologies are poised to advance rapid microbiology applications that will enable the industry to better trace contamination to the source.
Fink’s comments track with Food Technology’s survey outlook indicators. About 26% of Technology Trends Survey respondents say their companies plan to invest in advanced pathogen identification and detection technologies, including rapid and automated microbiology systems such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR), DNA/whole genome sequencing, and biosensors. Real-time continuous monitoring technologies, such as time/temperature, humidity, and gas level systems and devices, are expected to receive the next highest percentage (19%) of investment by food, beverage, and ingredient companies in 2025, according to survey respondents.
Three technology categories considered stalwarts of the processing industry also ranked high for 2025 food safety investment by industry respondents. At nearly 20% each, nonthermal processing technologies (e.g., high pressure processing, pulsed electric field, ultraviolet and light-based disinfection); thermal processing technologies (e.g., ohmic, infrared, high pressure thermal processing); and foreign materials detection systems (e.g., camera vision, X-ray) were identified as near-term areas of budget spending by survey participants.
The Near-Term Outlook: Optimistic
In 2025, the food industry is poised to make increased investments in cutting-edge technologies that promise to revolutionize food production, manufacturing, and distribution. Whether it’s AI, precision fermentation, or upcycling technologies, these advancements are expected to enhance efficiency, ensure food safety, and meet the growing demand for transparency and sustainability in the food supply chain. As industry continues to embrace these innovations, the future of the food system looks brighter than ever.ft
Tech Trends Research Methodology
Invitations to participate in Food Technology’s 2024 Technology Trends Survey were distributed online to Institute of Food Technologists (IFT) industry members working in food, beverage, and ingredient manufacturing and distribution, consulting, and technology development. Responses were collected and analyzed to determine trend indicators based on fully completed surveys submitted by 194 food industry professionals from multinational, national, and regional enterprises. The inaugural benchmark survey was conducted in June and July 2024 and participation was voluntary and anonymous.
Note: Questions were designed with a “check all that apply” format in which respondents were instructed to select every answer that pertains to them, resulting in percentages adding up to more than 100% during data analysis.
Outlook: Slightly Overcast?
Food Technology’s Technology Trends Survey also asked IFT members in the food, beverage, and ingredient industry to identify the biggest challenges or barriers to adoption or use of digital transformation technologies and biotechnology applications. Cost was cited as the number one barrier for both by more than 60% of the companies surveyed.
Top 5 Digital Technology Adoption Barriers
- Cost (69%)
- Integration of digital systems with legacy systems/equipment (53%)
- Employee reskilling and training (31%)
- Achieving interdepartmental buy-in (28%)
- Interoperability of systems (27%)
Top 5 Biotechnology Adoption Barriers
- Cost (63%)
- U.S. regulatory/labeling compliance (34%)
- Limited scalability and accessibility (34%)
- Consumer misperception/lack of public acceptance/education (33%)
- General manufacturing complexities (30%)
Hero Image: © beast01/istock/getty images plus
Authors
-

Julie Bricher Editor
is Science and Technology editor of Food Technology magazine (jbricher@ift.org).
Categories
-
Sustainability
-
Artificial Intelligence
-
Food Safety and Defense
-
Biotechnology
-
Novel Technologies
-
Issues & Insights
-
Food Technology Magazine
-
Food Processing and Technologies



