Membranes, Microfiltration, Microsieves, and More
PROCESSING
Membranes generally refer to materials with controlled ability to pass or retain molecules or particles of specific sizes. Familiar applications include microfiltration, ultrafiltration, and reverse osmosis, differing in the scale of substances that are retained. Reverse osmosis membranes, for example, can retain ions such as sodium and chloride, permitting production of pure water from sea water.
Bacteria and yeast, on the other hand, are retained by microfiltration membranes, permitting sterilization of liquids such as draft beer and water. The driving force in membrane separations is often pressure, but it also can be a concentration difference or an electric field, as in electrodialysis.
 Depending on the application, the retentate or the permeate may be the desired product. For example, in water treatment, the permeate is the purified water, while in concentration of fruit juices, the retentate is the concentrate.
Depending on the application, the retentate or the permeate may be the desired product. For example, in water treatment, the permeate is the purified water, while in concentration of fruit juices, the retentate is the concentrate.
Concentration of fruit and vegetable juices is limited by osmotic pressure, as the soluble solids become higher, and also by viscosity, which impacts mass transfer and pressure drop through the equipment. Because membrane concentration does not involve heat, as does evaporation, there is less loss of flavor. In most cases, this is desirable, but in some situations the flavor may be undesirable. Examples are the use of apple juice concentrate, grape juice concentrate, and sweet potato concentrate as sweeteners in beverages. The natural sweeteners are attractive on the label and can provide some of the recommended fruit and vegetable servings, but a bland taste may be required as well. In such cases the concentrate may be deliberately finished by thermal evaporation to remove some volatile flavors.
Pervaporation
Pervaporation is a membrane separation process in which small volatile components are selectively removed from a mixture by diffusing through a semi-permeable sheet of polymer, such as polydimethylsiloxane. On one side of the membrane is an aqueous solution while on the other side is either a sweep gas or a vacuum. The small molecules vaporize and move through the membrane while water and larger molecules are rejected. Such a process could remove flavors from a juice, if desired, and even recover a concentrated essence by condensing the permeate stream.
Electrodialysis
Simple dialysis relies on the concentration difference between a dilute solution on one side of a semi-permeable membrane and a more concentrated solution on the other side. An example is purification of human blood by removal of small molecules such as urea while proteins are retained. In electrodialysis, positively and negatively charged membranes are alternated in a stack between electrodes. In an electric field, positively charged ions attempt to migrate towards the negative electrode and negatively charged ions migrate towards the positively charged electrode. The positively charged ions pass through the positively charged membrane but are retained by the negatively charged membrane and vice versa. Ions accumulate in the spaces between the membranes leading to a separation. Flux rates are relatively low, and some membrane materials can foul after a period of operation. To reduce fouling, the direction of the electric field can be reversed.
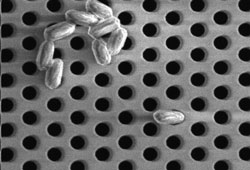
 Microsieves
Microsieves
One of the more intriguing variants of membranes is offered by SieveCorp of the Netherlands, according to Jorine Zandhuis ([email protected]). SieveCorp fabricates sieves from 6-in disks of silicon using the semiconductor manufacturing process of microlithography and etching. The disks are only 1 μm thick, so pressure drop through the very precise pores is small. Pores are etched to have an exact size, which may lie between 0.25 μm and 0.8 μm. On a single disk, there may be billions of pores. Flux rates are said to be 180 L/hr per disk. Ninety disks provide 1 m2 of membrane area. Pressures are said to be 0.5 bar or about 7 psi.
In U.S. units, fluxes are typically expressed in gal per sq ft per day (GFD). SieveCorp’s rates of 16 m3/m2/hr (MMH) (for an array of 90 disks) are equivalent to 9,428 GFD, a very high rate. The major application promoted for SieveCorp is filter sterilization of milk, whey, beer, clear juices, and parenteral nutrition fluids (solutions that are injected into patients). The etched pores retain bacteria and spores while passing proteins, fats, salts, and sugars.
An interesting engineering issue is how to uniformly distribute flow among so many modules. The reason for a size limitation on the disks is the availability of silicon wafers in a standard size of 6 in. Other types of membranes experience some economy of scale as area and capacity are increased.
SieveCorp has developed a high frequency pulsing technique to back flush the disks and remove debris that might otherwise clog the pores. Flow is across the face of the disk to also assist mass transfer.
--- PAGE BREAK ---
Other Membrane Configurations
In addition to cross-flow across flat surfaces, other membranes are fabricated in tubes that may be 0.5 in, hollow fibers about the size of human hairs, and spiral wound modules. Wide tubes are used where there may be suspended solids that would otherwise clog flow passages. Typically the membrane may be deposited on the outside or inside of a porous fiberglass tube that provides mechanical support.
Many polymer membranes have a thin active layer that is very tight and a larger, porous support layer that may even be a different polymer. Dynamic membranes are formed in place by deposit of a layer of solids on a porous support. Still other membranes are fabricated from sintered powder metal or ceramics. These are especially useful in cleaning up corrosive solutions such as caustic and acids used in cleaning in place (CIP) of food and dairy equipment. Metal and ceramic filters can also withstand higher temperatures than can polymer membranes.
Hollow fiber membranes are typically self-supporting because of their small diameter. Very large areas can be fabricated in a small volume using hollow fibers. Flow may be from outside in or the reverse, depending on pressures required and viscosity of the feed.
Spiral wound modules also have a high area per unit volume. Flat sheets of polymer are separated by flexible porous layers and then wound around a hollow feed tube. The assembly is held inside a pressure-resistant shell.
Especially with hollow fibers, but also for some other forms of membranes, pre-filtration is often a good idea. In general, it is difficult to make too great a change in any process, whether it be size reduction, mixing, or filtration. Thus, it is usually good practice to pre-break feed material that is being ground, and grind it in several steps.
In mixing, it is often helpful to pre-mix minor and micro ingredients before dispersing in bulk or major ingredients. In filtration and separation, it is often helpful to remove large particles using a relatively coarse filter, or some other technique, before applying a relatively tight membrane that might easily clog. Thus a typical membrane separation process may consist of several stages of filtration, perhaps using different materials and configurations.
Back flushing can help, but membranes still can foul. When flux rates begin to decline to unacceptable levels, the membranes must be cleaned or replaced. Accordingly, membrane materials must be resistant to effective cleaning procedures. Typically, hot water and mild detergents are adequate for cleaning most membranes.
In operation, it is often tempting to increase feed pressure as membrane flux begins to decline, but this may be counterproductive, as increased pressure may cause membranes to compact, decreasing flow still further. Back flushing or cleaning is a better approach, which may prolong membrane life and maintain a higher net production rate than carelessly increasing pressure.
Membranes as Diffusers
Polymer membranes can be used to disperse air into bioreactors, such as water treatment plants. The same fine pores that enable separations of particles and solutes can produce very fine bubbles that enhance mass transfer. GE, among other firms, offers membrane bioreactor waste water treatment systems that have a small footprint and a high capacity for handling industrial wastes, such as food plants produce, according to Yuvbir Singh, general manager, engineered systems—water and process technologies for GE Power & Water. In some cases, existing treatment systems can be retrofitted within the same space and increase capacity.
The first selective membranes were made of cellulose acetate and were applied to desalination of water. Since that work in the 1960s, there have been great strides made in membrane materials, including the various polymers, ceramics, metals, and silicon. Flux rates have been greatly improved as has selectivity. Processes based on membranes are used for sterilizing, concentration, and purification of water, milk, and juices. Concentration of whey, a waste from cheese making, is a major application, as is concentration of raw milk intended for cheese as a way of reducing transportation costs and the production of whey at the cheese plant. With the popularity of Greek yogurt, a new source of whey has been created, and thus a new opportunity for membrane concentration. Membrane separations are usually energy efficient because they do not involve a phase change, and so they are attractive to firms seeking sustainable processes.
 J. Peter Clark, Ph.D., CFS,
J. Peter Clark, Ph.D., CFS,
Contributing Editor,
Consultant to the Process Industries, Oak Park, Ill.
[email protected]
